Account Type and Gas Fee Management
Wallet Account types and gas fee management can be complex topics—especially in on-chain payment scenarios. To help developers navigate these challenges, USDCKit offers a set of simplified and opinionated solutions. This guide walks you through those options so you can quickly understand the trade-offs and choose the most suitable approach for your use case.
Understanding Account Types
USDCKit (with built-in Circle Wallet) currently supports 2 types of accounts for EVM blockchains:
EOA (Externally Owned Account)
Definition: A traditional wallet account controlled by a user's private key. Features:
- Users must hold and manage native tokens (e.g., ETH, SOL) to pay gas fees. It usually costs less when making transactions compared to SCA
- Simpler to integrate but less flexible for advanced UX designs
SCA (Smart Contract Account)
Definition: Wallet account governed by smart contracts rather than just private keys. Features:
- Support different gas abstraction methods to simplify the gas payment experience (subsidize gas for your users, pay with USDC). But with higher gas cost compared to EOA
- Enable flexible authorization, batching, and automation
- Ideal for abstracting blockchain complexity from end-users
As described in the features of these 2 account types, there are many considerations when choosing the most suitable account type. You can refer to this page to understand more. However, gas management is one of the most critical factors to consider, and we will use that to elaborate on how to make the right choice for your business.
Decision Flow: Account Type and Gas Payment
Gas is the fee required to execute transactions or smart contract operations on a blockchain. Gas management refers to how those fees are paid. The gas management logic and payment experience that you desire directly informs which account type is most suitable for your application. Go through the following section to make a decision:
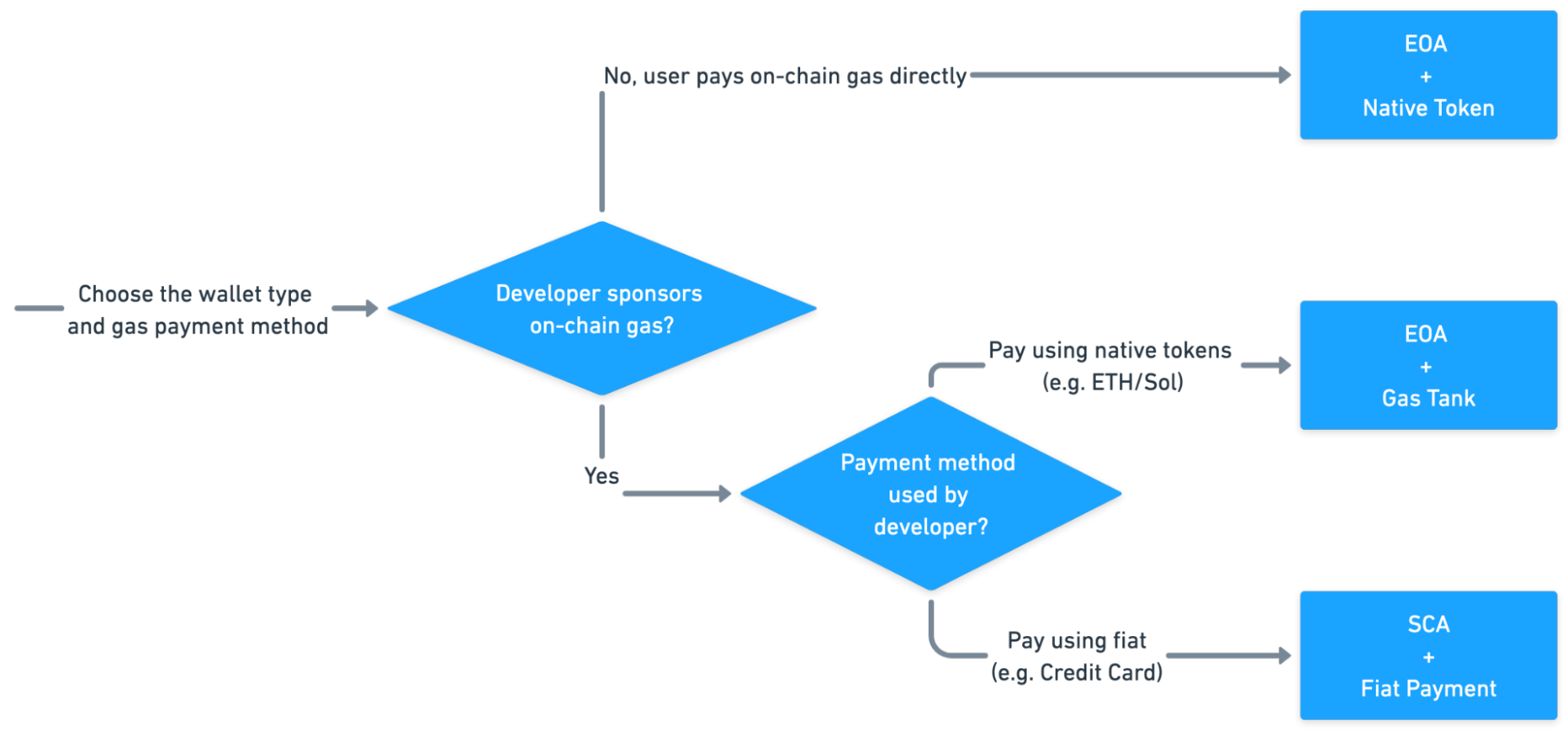
The above diagram can be summarized into the following table, and it explains how to manage your gas in each scenario in detail:
| Scenario | EOA + Native Token | EOA + Gas Tank | SCA + Fiat Payment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Developer Sponsors Gas | ❌ No | ✅ Yes | ✅ Yes |
| Payment Method | Native Token | Native Token | Fiat |
| Account Type | EOA | EOA | SCA |
| Gas Cost | Normal (1x) | Slightly More Expensive (~2x) | Expensive (~4x-8x) |
| Transaction Processing Time | Normal (1x) | Slow (~2x) | Normal (~1x) |
| Sample Business Scenarios | The developer provisions internal accounts for each user, enabling them to deposit and manage their token assets. The user will manage the native tokens in these accounts. | The developer maintains an on-chain treasury containing various native tokens, which is used to directly sponsor gas fees for business operations. | The developer prefers not to manage on-chain gas fees, as service fees are collected in fiat and there is no token treasury. Instead, they would like to cover all on-chain costs using fiat. |
| How To Manage Wallet Accounts and Gas |
|
|
|
Sample Code Implementation
Refer to the sample code below to understand how to implement the above 3 different gas fee management logics:
EOA wallet pays gas with native token
// Create EOA
const account = await client.createAccount({ accountType: 'EOA' })
// `account` pays for fees
await client.transfer({
from: account,
to: '0x....',
// Optional. Defaults to estimating gas required
gas: 123n,
// Optional. Defaults to estimating gas fee required
fees: { maxFeePerGas: 123n, maxPriorityFeePerGas: 123n },
})
EOA wallet pays gas with gas tank
// Create EOA
const account = await client.createAccount({ accountType: 'EOA' })
await client.transfer({
from: account,
to: '0x....',
// Optional. Defaults to estimating gas required
gas: 123n,
// Required.
// `gasTankAccount` sends native tokens equal to the gas fee estimate `HIGH`
// After native token transfer, `account` execute the transaction
// NOTE: This may fail due to non-atomic and changing gas fees
fees: FEE_LEVEL_WITH_PREPARE({
level: 'HIGH',
account: gasTankAccount,
}),
})
SCA wallet pays gas with Circle Gas Station
// Create SCA
const account = await client.createAccount({ accountType: 'SCA' })
// `account` pays for fees via Circle Gas Station
await client.transfer({
from: account,
to: '0x....',
// Required. -1n disables explicit gas limits
gas: -1n,
// Required. -1n disables explicit fee limits
fees: { maxFeePerGas: -1n, maxPriorityFeePerGas: -1n },
})